The Ultimate Guide to SPACs: Understanding the Future of Investing
If you’re an investor, you might have come across the term SPACs. And if you’re not, don’t worry, we’re here to demystify the topic for you. SPACs or Special Purpose Acquisition Companies are making headlines in the investment world. They are also known as “blank check companies,” and for good reason. SPACs are an innovative investment vehicle that allows investors to participate in a merger or acquisition of a private company.
In this post, we’ll cover everything you need to know about SPACs, including their definition, how they work, their advantages and disadvantages, and what the future holds for this exciting new investment opportunity.
What are SPACs, and How do They Work?
SPACs are a type of blank check company created to raise capital through an initial public offering (IPO) to finance the acquisition of a private company. Essentially, a SPAC is a shell company with no operations or commercial activities, but with cash raised from investors in an IPO. The sole purpose of the SPAC is to use these funds to acquire a private company and take it public.
The SPAC structure includes a sponsor, who is typically an experienced investor or a group of investors, who create the SPAC and raise capital through the IPO.
The sponsor’s role is to find a suitable target company and negotiate a merger or acquisition.
Once the target company is identified, the SPAC acquires it through a reverse merger, with the target company becoming a publicly-traded company, and the SPAC ceasing to exist.
Advantages of Investing in a SPAC
Investing in a SPAC can be an attractive proposition for several reasons.
Firstly, it provides investors with an opportunity to invest in private companies that are not publicly traded, thereby providing access to potentially high-growth companies.
Secondly, investing in a SPAC can be less risky than investing in individual private companies since the SPAC sponsor usually has a good track record in identifying profitable targets.
Thirdly, investors can participate in the potential upside of the merger or acquisition while minimizing their downside risk. This is because SPACs usually have a redemption option that allows investors to redeem their shares for cash if they do not approve of the target company.
Disadvantages of Investing in a SPAC
Although investing in a SPAC has several advantages, there are also some disadvantages to consider.
Firstly, there is a lack of transparency in the SPAC’s target company selection process. Since the SPAC is a shell company with no commercial activities, investors have no say in the target company selection process. This lack of transparency can lead to potential conflicts of interest.
Secondly, investing in a SPAC can be riskier than investing in other assets, such as stocks or bonds, as the SPAC has no commercial activities or operations. This means that there is no historical financial data available, and the success of the investment depends on the sponsor’s ability to identify and acquire a profitable target company.
SPACs vs. Traditional IPOs
SPACs have become increasingly popular in recent years as an alternative to traditional IPOs. The main difference between a SPAC and a traditional IPO is that a SPAC is a shell company created solely to acquire a private company, while a traditional IPO is the process by which a private company goes public by selling shares of its stock to the public.
The traditional IPO process is lengthy and can take months or even years to complete, with significant upfront costs. On the other hand, the SPAC process is much faster and more cost-effective, as the SPAC has already gone through the IPO process, and the target company does not have to go through the lengthy and expensive traditional IPO process.
In addition, traditional IPOs can be risky for investors, as the stock price can be highly volatile in the initial days after the IPO. In contrast, SPACs provide investors with a more stable investment opportunity, as the merger or acquisition of the target company is usually planned in advance, providing investors with a more predictable investment.
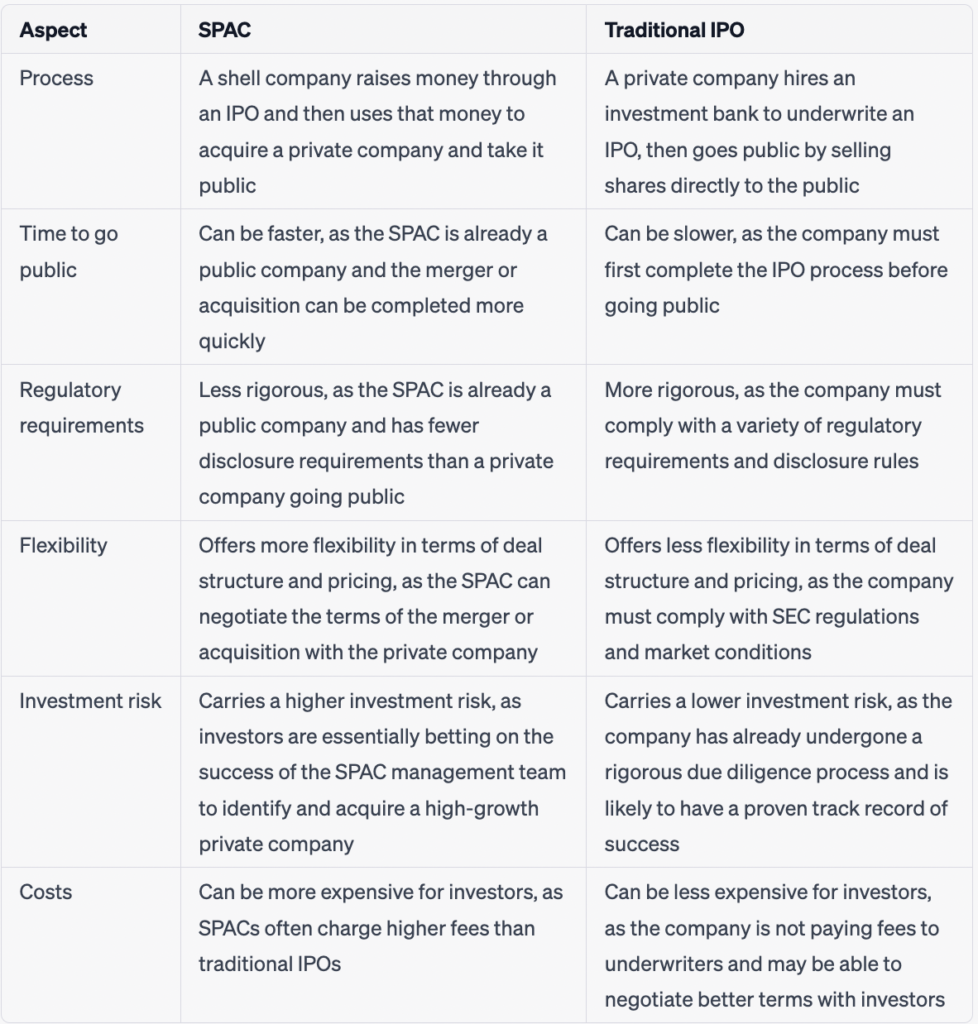
It’s worth noting that SPACs and traditional IPOs are not mutually exclusive, and some companies may choose to explore both options before ultimately deciding which route to take. Additionally, both SPACs and traditional IPOs have their own set of advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important for companies and investors alike to carefully consider their options before making a decision.
SPACs in the Current Market
SPACs have gained significant attention in recent years, with the number of SPAC IPOs increasing from 59 in 2019 to 248 in 2020. This trend has continued in 2021, with 331 SPAC IPOs in the first quarter of the year alone.
The increase in SPAC IPOs can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to an economic downturn, making traditional IPOs less attractive to companies looking to go public. Secondly, low-interest rates have made it easier for SPACs to raise capital, as investors are looking for higher returns than traditional investments.
However, the increase in SPAC IPOs has led to concerns about potential risks for investors. Regulators have started to scrutinize the SPAC market, and there have been calls for increased disclosure requirements and tighter regulation.
What are some examples of SPACs
There have been many high-profile SPACs that have made headlines in recent years. Here are a few examples of well-known SPACs:
- Churchill Capital Corp IV (CCIV): This SPAC made headlines in early 2021 when it announced a deal to merge with electric vehicle maker Lucid Motors, valuing the company at over $24 billion.
- Social Capital Hedosophia Holdings Corp V (IPOE): This SPAC, led by billionaire investor Chamath Palihapitiya, announced a deal to take the online real estate platform OpenDoor public in late 2020. The deal valued OpenDoor at over $4 billion.
- Pershing Square Tontine Holdings (PSTH): This SPAC, led by billionaire hedge fund manager Bill Ackman, raised a record-breaking $4 billion in its IPO in 2020. The SPAC has not yet announced a merger or acquisition target.
- VG Acquisition Corp (VGAC): This SPAC, led by former Disney CEO Michael Eisner, announced a deal to merge with sports betting company DraftKings in early 2020. The deal valued DraftKings at over $3 billion.
- SPACs sponsored by celebrities: Several well-known celebrities, including Shaquille O’Neal, Serena Williams, and Alex Rodriguez, have sponsored SPACs in recent years. These SPACs typically target companies in the entertainment, media, and technology sectors.
Related Posts
Conclusion
In conclusion, SPACs are a relatively new investment vehicle that has gained significant attention in recent years. They provide investors with an opportunity to invest in high-growth private companies that are not publicly traded while minimizing their downside risk.
However, investing in SPACs does come with its own set of risks, including a lack of transparency in the target company selection process and the potential for conflicts of interest. Investors should carefully consider these risks before investing in a SPAC.
As the popularity of SPACs continues to grow, regulators will likely increase their scrutiny of the market, leading to increased disclosure requirements and tighter regulation. Nonetheless, SPACs remain an exciting investment opportunity, and investors should continue to monitor this space for potential opportunities.









